Server Technologies
Overview
- Server
- Framework types
- PHP
- Java Servlets
- JS
pdf
Role of servers
- The Web is not just a set of static HTML documents !
- Server-side programs allow:
- to process form submissions;
- to display in a uniform way all the pages of a site;
- offer interactive applications;
- to allow the user to add or modify content; etc.
- to do more advanced things like Webstrates
- online editing
- collaborative editing
- wrap any program into an online version
Web server
- Keywords: Apache, NGINX, HTTPD, IIS
- Implements the HTTP protocol: GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE …
- Returns information in response to requests
- Dialog with the browser
- Returns a file in response to a GET
- Receives a file after a POST
- Apache is the best known and most common
- NginX is the runner-up
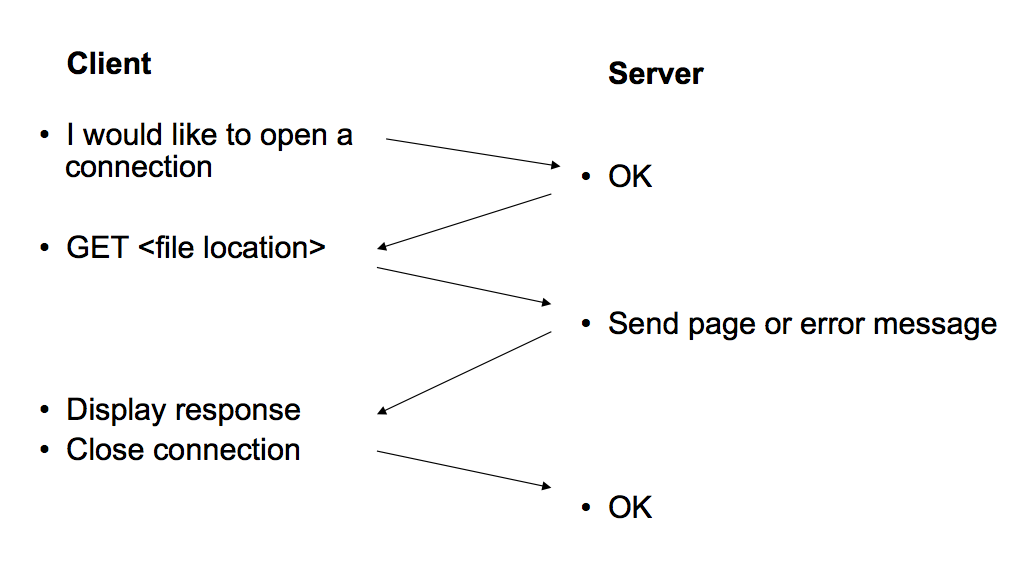
Principle
![]()
Request: example
Request:
GET /path/file.html HTTP/1.0
From: someuser@jmarshall.com
User-Agent: HTTPTool/1.0
<<< blank line here
Response:
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Date: Fri, 31 Dec 1999 23:59:59 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 1354
<html>
<body>
<h1>Happy New Millennium!</h1>
(more file contents)
.
.
.
</body>
</html>
Return code
- HTTP/1.0 200 OK
- HTTP/1.0 301 Moved Permanently
- HTTP/1.0 302 Moved Temporarily
- HTTP/1.0 400 Bad Request
- HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized
- HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden
- HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found
- HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Server Error
Web servers in practice
- your code in the “Server” lab, started on the command line
- a service from your OS: httpd in Linux/Mac, IIS in Windows
- a complex application: L/M/WAMP = combination of http server on port 80, SQL server on port 3306 and PHP interpreter
- a virtual machine in DSI for your personal pages
- a service in the cloud for companies
Example of a server started on this machine and used with curl
Apache Configuration
ThreadsPerChild 250
MaxRequestsPerChild 0
Listen 80
ServerRoot "/www/Apache22"
DocumentRoot "/www/webroot"
ServerName localhost:80
ServerAdmin admin@localhost
ErrorLog logs/error.log
LogLevel error
LoadModule alias_module modules/mod_alias.so
...
<IfDefine SSL>
LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so
</IfDefine>
Apache Config
DefaultType text/plain
<IfModule dir_module>
DirectoryIndex index.html index.php index.aspx
</IfModule>
IndexIgnore .htaccess
<FilesMatch "^.ht">
Order allow,deny
Deny from all
</FilesMatch>
<Directory>
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride all
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
Satisfy all
</Directory>
Apache Config
<Directory "/www/webroot">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride all
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
<IfModule mime_module>
TypesConfig conf/mime.types
AddType application/x-compress .Z
AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz
</IfModule>
Include conf/extra/httpd-autoindex.conf
...
#config du module PHP
#config du module SSL
#config du module SQL
#config du module phpMyAdmin
Per folder
By default, we display index.html or index.htm or index.php or …
Otherwise, the list of files is displayed if the enumeration is allowed
Folder behavior can be specified without changing the general configuration
- Enable the enumeration of files
- Change the appearance of the URL
- Request authentication
- Sending errors
- Serve custom media types
- Allow server-side-includes
- Make a redirection
<Directory /var/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
allow from all
</Directory>
Cookies
- Information from the server stored on your machine
- You guess the security problems …
- Cookie session: the cookie is valid for a session, ie a set of connections for a while, or without long interruption
- Persistent cookie: the cookie stays forever
- Secure cookie: cookie restricted to HTTPS connection
Cookie example
Here is the HTML of the example, JS follows on next slide. You see a list selector and an input, the cookie keeps what element was last selected or input.
<form id="form" action="choose">
<label for="studlab">Lab name: </label>
<select class="form-control" id="studlab" name="studlab">
<option selected="selected">Choose</option>
<option value="html">Html Lab (html)</option>
<option value="js">JavaScript Lab 1 (js)</option>
<option value="js2">JavaScript Lab 2 (js2)</option>
<option value="server">Server Lab (server)</option>
<option value="server2">Server2 Lab (server2)</option>
</select><br>
...
<input id="student" type="text" name="student" value="@@@@"
hidden/>
Cookie, the script
<script type="application/ecmascript">
function setCookie(name, value) {
document.cookie = name + "=" + encodeURIComponent(value) +
"; path=/; expires=" + expiry.toGMTString();
}
function subm(actionname) {
setCookie("studlab", form.studlab.value);
setCookie("studaction", actionname);
...
}
function getCookie(name) {
var re = new RegExp(name + "=([^;]+)");
var value = re.exec(document.cookie);
return (value != null) ? unescape(value[1]) : null;
}
var form = document.getElementById("form");
var lab = getCookie("studlab");
if (lab) {
form.studlab.value = lab;
console.log("retrieved cookie studlab="+lab);
}
</script>
Cache and proxy
- Cache:
- everything can be cached: any kind of data, fragments or whole files
- as many cache level as you want: Telecom, Internet provider, …
- commercial cache (CDN): Akamai, Amazon, Azure, OVH, L3, ATT, Deutsche Telekom …
- Proxy: the protocol can be relayed by an intermediate machine, for example to make visible from the outside only one machine, or to implement caching
- Your internet box acts as a proxy
- A load balancer at Google acts as a proxy
Programming languages
CGI (Common Gateway Interface): standardized interface allowing Web server communication with a program running on the server
CGI allows you to use any programming language (compiled like C, C ++, Java, or interpreted as Perl, Python, Ruby, etc.) to implement server-side actions.
But some languages are more suited to Web development:
- have functions specifically dedicated to HTTP, HTML, etc.;
- integrate more effectively and more conveniently with the Web server (with software extensions);
- have a specially designed syntax, which mixes HTML code sent such which and programming instructions interpreted.
Whatever technology is used, the code of the program is not accessible by the web browser, only the result of his execution.
Server-side languages
- PHP: one of the most popular languages, integrates very easily with Apache (free)
- ASP and ASP.NET: intended to be used with IIS (Microsoft, commercial)
- ColdFusion (Adobe, commercial)
- JSP (Java Server Pages): allows to mix Java instructions and HTML code; requires a Java application server (eg, Tomcat) in more Apache (Sun, free)
- Java Servlets: Real Java programs, rather for complex server-side applications with little side interaction customer; requires a Java application server in addition to Apache (Sun, free)
- JS with node.js
Frameworks
- The languages presented above remain fairly basic and generic.
- They do not necessarily encourage a clean organization of a website.
- Framework: set of a programming language, a library of functions, external tools, good practices to follow…
- Allows you to abstract the creation of a web page.
- Usually follows the MVC model.
- Sometimes includes client-side JavaScript code generation for direct creation of a highly dynamic web application (eg, form validation); Ajax integration also.
- Highly recommended for creating complex applications… but also complex to master !
Popular Frameworks
- ASP.NET: DotNetNuke
- ColdFusion: Model-Glue, Fusebox
- Java: Struts, Spring, JavaServer Faces, Google Web Toolkit
- Perl: Catalyst
- PHP: CakePHP, Symphony, Zend, Laravel
- Python: Django
- Ruby: Ruby on Rails (very influential !)
- Smalltalk: Seaside
- … and many more !
CMS
CMS (Content Management System)
Create websites without writing code
Features:
- simplified page editing (wiki or bbcode syntax, or control JavaScript rich text);
- adding external content (images, additional documents, etc.);
- user management, access control, etc. ;
- modules for managing forums, blogs;
- ready-to-use graphical themes;
- version control.
Depending on the CMS, extensions can be numerous.
Some specialized CMS: blogs (Wordpress, Dotclear, Movable Type, TypePad), e-commerce (PrestaShop, Magento), forums (phpBB, MyBB), etc.
Example of a CMS: Wordpress
Show source of PACT wp site.
CMS and Web programming
Even when using a CMS, it is useful to know Web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, server-side language):
- to create your own CSS styles (almost indispensable);
- to develop complex, site-specific applications;
- to develop or adapt small extensions;
- to understand what happens in case of problems;
- to control security;
- to ensure that pages meet certain conditions (W3C validity, accessibility).
Misc CMS
CMS vs. Wiki: fuzzy border
Choice of a CMS: license, programming language, existence of extensions specific to your problem
Disadvantages:
- Slower than a site in pure HTML
- Security breaches: Monitor security updates and apply updates often
- Orphaned software: without frequent updates, such software is a danger
- Migration to another system may be expensive
- Not suitable for all purposes
- Beware of the dependence on a developer (need to document, choice of languages)
PHP example
- PHP script: HTML document (for example), in which is embedded PHP code.
- The PHP code is inside a pseudo-tag
<?php ...?> (or <?= ...?> which is a shortcut for <? echo ...?>).
![]()
PHP
- A PHP script is a sequence of instructions completed by semicolons.
- These instructions contain variable or constant elements, can have conditional statements or loops.
- HTTP parameters can be retrieved in PHP thanks to associative tables $_GET and $_POST.
- The values in these tables can be simple variables or indexed tables.
echo "<p>Votre login est : " . $_POST["login"] . "</p>";
echo "<p>Vous avez coché les genres : ";
for($i=1;$i<=count($_POST[’genre’]);$i=$i+1) {
echo $_POST[’genre’][$i] . " ";
}
echo "</p>";
Servlets
We will talk of the servlets even though the technology has lost momentum. But all the notions in servlets exist in node.js and in other systems.
The only jobs that remain in Java are about servlets and large information systems.
- What is a servlet?
- Interaction with the customer
- Structure and operation
- Store the customer’s state
- Communication with the server
- Server configuration
- Call a servlet
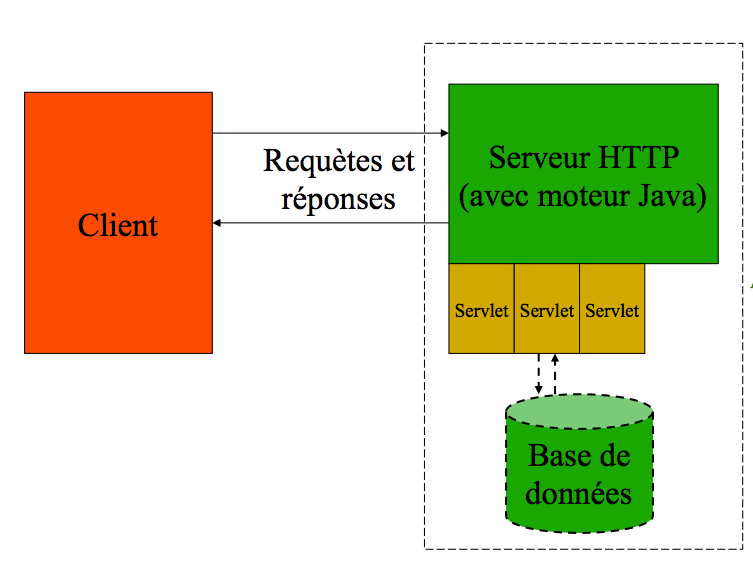
What is a servlet?
![]()
What is a servlet?
- A Java class, implementing javax.servlet.Servlet
- Usually a subclass of HttpServlet
- An address on the server
- Called by one or more HTML page(s)
- Main and necessary classes are on the server, but are not downloaded
Interaction with the customer
- Requests and responses
- GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
- Threads
Operations
- Customer request
- [The server loads the servlet and starts its thread]
- The server sends the request to the servlet
- The servlet sends the response to the server
- Back to the client
- Shutdown: the server stops active servlets
Call a servlet
From a browser: the servlet renders an HTML page (or content with mime type)
From an HTML page: the servlet is “buried” in a page
- <a href=“servURL”> …
- <form action = “servURL” method = “post” > …
node.js
- Created in reaction to Java Servlet, very used and much criticized
- Many similarities, but simpler
- Only handles HTTP requests
- Lower level than Tomcat: mix the HTTP daemon with the servlet side
- Implemented with non-blocking IOs
- Lighter
File Server example
var http = require("http"),
fs = require("fs");
http.createServer(function(request,response){
var full_path = process.cwd()+request.url;
path.exists(full_path,function(exists){
if(!exists){
response.writeHeader(404, {"Content-Type": "text/plain"});
response.write("404 Not Found\n");
response.end();
}
else{
... seeNextSlide ...
}
});
}).listen(8080);
console.log("Server Running on 8080");
Server 2
fs.readFile(full_path, "binary", function(err, file) {
if(err) {
response.writeHeader(500, {"Content-Type": "text/plain"});
response.write(err + "\n");
response.end();
} else{
response.writeHeader(200);
response.write(file, "binary");
response.end();
}
});
Request
Class: http.IncomingMessage (!Warning! not ClientRequest)
- Event: ‘close’
- message.httpVersion
- message.headers
- message.trailers
- message.setTimeout(msecs, callback)
- message.method
- message.url
- message.statusCode
- message.socket
Response
Class: http.ServerResponse
- Event: ‘close’
- Event: ‘finish’
- response.writeContinue()
- response.writeHead(statusCode, [reasonPhrase], [headers])
- response.setTimeout(msecs, callback)
- response.statusCode
- response.setHeader(name, value)
- response.headersSent
- response.sendDate
- response.getHeader(name)
- response.removeHeader(name)
- response.write(chunk, [encoding])
- response.addTrailers(headers)
- response.end([data], [encoding])
Sessions and cookies
Not in basic node.js
Many solutions:
- Connect module: developed by the same people as Express
- Express module: very simple, very used, heavier
- Geddy module: more complete
Choice: question of taste, of project context
It moves very fast
Summary of the lesson
- Server, function, request, headers, return code, configuration
- Cookie, usage, cache, proxy
- Server-side languages, frameworks, CMS
- PHP, Servlet, node.js